-
Faulty ignition:
- Incorrect valve timing
- Fouled, shorted or improperly gapped spark plugs
- Incorrect valve clearance (valve lash adjuster assembly)
- Leaks in intake or exhaust valves
- Leaks in cylinders
| Last Modified: 11-20-2023 | 6.11:8.1.0 | Doc ID: RM100000001JQHX |
| Model Year Start: 2020 | Model: Camry | Prod Date Range: [09/2019 - ] |
| Title: 2GR-FKS (ENGINE MECHANICAL): ENGINE: ON-VEHICLE INSPECTION; 2020 - 2024 MY Camry [09/2019 - ] | ||
ON-VEHICLE INSPECTION
CAUTION / NOTICE / HINT
CAUTION:
To prevent injury due to contact with an operating V-ribbed belt or cooling fan, keep your hands and clothing away from the V-ribbed belt and cooling fans when working in the engine compartment with the engine running or the engine switch on (IG).
PROCEDURE
1. INSPECT ENGINE COOLANT
2. INSPECT ENGINE OIL
3. CHECK BATTERY CONDITION
4. INSPECT SPARK PLUG
5. INSPECT AIR CLEANER FILTER ELEMENT SUB-ASSEMBLY
(a) Remove the air cleaner filter element sub-assembly.
(b) Visually check that the air cleaner filter element sub-assembly is not damaged or excessively oily.
HINT:
- If there is any dirt or clogs in the air cleaner filter element sub-assembly, clean it with compressed air.
- If any dirt or clogs remain even after cleaning the air cleaner filter element sub-assembly with compressed air, replace it.
(c) Install the air cleaner filter element sub-assembly.
6. INSPECT V-RIBBED BELT
7. INSPECT V-RIBBED BELT TENSIONER ASSEMBLY
(a) Remove the V-ribbed belt.
(b) Turn the V-ribbed belt tensioner assembly clockwise and counterclockwise and check that it turns smoothly and does not catch.
HINT:
If the V-ribbed belt tensioner assembly does not turn smoothly or catches, replace the V-ribbed belt tensioner assembly.
(c) Install the V-ribbed belt.
8. INSPECT VALVE LASH ADJUSTER ASSEMBLY NOISE
(a) Rev up the engine several times. Check that the engine does not emit unusual noises.
(b) If unusual noises occur, warm up the engine and idle it for 30 minutes or more, then perform the inspection.
HINT:
If any defects or problems are found during the inspection, perform valve lash adjuster assembly inspection.
9. INSPECT IGNITION TIMING
NOTICE:
- Check the ignition timing with the cooling fans off.
- Turn off all the electrical systems and the A/C.
- When checking the ignition timing, the transaxle should be in neutral or park.
(a) Warm up and stop the engine.
(b) Connect the Techstream to the DLC3.
(c) Start the engine and run it at idle.
(d) Turn the Techstream on.
(e) Enter the following menus: Powertrain / Engine / Data List / Ignition Timing Cylinder #1
Powertrain > Engine > Data List
|
Tester Display |
|---|
|
Ignition Timing Cylinder #1 |
Standard Ignition Timing:
12 to 24° BTDC at idle
(f) Check that the ignition timing advances immediately when the engine speed is increased.
(g) Enter the following menus: Powertrain / Engine / Active Test / Activate the TC Terminal / ON.
Powertrain > Engine > Active Test
|
Active Test Display |
|---|
|
Activate the TC Terminal |
|
Data List Display |
|---|
|
Ignition Timing Cylinder #1 |
(h) Monitor Ignition Timing Cylinder #1 of the Data List.
Standard Ignition Timing:
8 to 12° BTDC at idle
10. INSPECT ENGINE IDLE SPEED
NOTICE:
- Check the idle speed with the cooling fans off.
- Turn off all the electrical systems and the A/C.
- When checking the idle speed, the transaxle should be in neutral or park.
(a) Warm up and stop the engine.
(b) Connect the Techstream to the DLC3.
(c) Start the engine and run it at idle.
(d) Turn the Techstream on.
(e) Enter the following menus: Powertrain / Engine / Data List / Engine Speed.
Powertrain > Engine > Data List
|
Tester Display |
|---|
|
Engine Speed |
(f) Read the value displayed on the Techstream.
Standard Idle Speed:
650 to 750 rpm
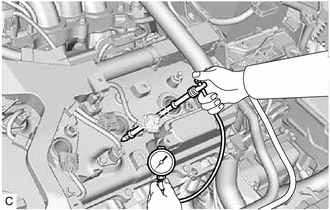
11. INSPECT COMPRESSION
NOTICE:
Keep the spark plug holes free of foreign matter when measuring the compression pressure.
(a) Warm up and stop the engine.
(b) Check for DTCs.
(c) Remove the 6 spark plugs.
|
(d) Check the cylinder compression pressure. (1) Insert a compression gauge into the spark plug hole. (2) Connect the Techstream to the DLC3. (3) Turn the engine switch on (IG). (4) Turn the Techstream on. (5) Enter the following menus: Powertrain / Engine / Active Test / Check the Cylinder Compression / Start. Powertrain > Engine > Active Test
(6) Depress and hold the brake pedal, and push the engine switch. Then check the compression pressure. Standard Compression Pressure: 1400 kPa (14.3 kgf/cm2, 203 psi) Minimum Compression Pressure: 1050 kPa (10.7 kgf/cm2, 152 psi) Pressure Difference between Each Cylinder: 200 kPa (2.0 kgf/cm2, 29 psi) or less NOTICE:
(7) If the cylinder compression is low, pour a small amount of engine oil into the cylinder through the spark plug hole then inspect the cylinder compression pressure again. HINT:
|
|
(e) Install the 6 spark plugs.
(f) Clear the DTCs.
NOTICE:
After the inspection, clear the DTCs, check for DTCs again and make sure the normal system code is output.
12. INSPECT CO/HC
HINT:
This check determines whether or not the idle CO/HC complies with regulations.
(a) Start the engine.
(b) Run the engine speed at 2500 rpm for approximately 180 seconds.
(c) Insert a CO/HC meter testing probe at least 40 cm (1.31 ft.) into the tailpipe during idle.
(d) Immediately check the CO/HC concentration at idle and then at an engine speed of 2500 rpm.
HINT:
When performing a 2 mode test (with the engine idling/running at 2500 rpm), the measurement procedures are determined by applicable local regulations.
If the CO/HC concentration does not comply with the regulations, perform troubleshooting in the order given below.
(1) Check for DTCs.
(2) See the following table for possible causes, then inspect the applicable parts and repair them if necessary.
|
CO |
HC |
Problem |
Cause |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Normal |
High |
Rough idle |
|
|
Low |
High |
Rough idle (Fluctuating HC reading) |
|
|
High |
High |
Rough idle (Black smoke from exhaust) |
|
|
|
|
![2018 - 2024 MY Camry [06/2017 - ]; 2GR-FKS (COOLING): COOLING SYSTEM: ON-VEHICLE INSPECTION](/t3Portal/stylegraphics/info.gif)