- Transponder Key Amplifier
| Last Modified: 08-28-2024 | 6.11:8.1.0 | Doc ID: RM100000000VJJA |
| Model Year Start: 2016 | Model: Sienna | Prod Date Range: [12/2015 - ] |
| Title: THEFT DETERRENT / KEYLESS ENTRY: SMART KEY SYSTEM(for Start Function): SYSTEM DESCRIPTION; 2016 - 2020 MY Sienna [12/2015 - ] | ||
SYSTEM DESCRIPTION
1. PUSH-BUTTON START DESCRIPTION
(a) The push-button start uses a push-type engine switch, which the driver can operate by merely carrying the electrical key. This system consists primarily of the power management control ECU, engine switch, steering lock ECU, electrical key, ACC relay, IG1 relay, IG2 relay and certification ECU (smart key ECU assembly). The power management control ECU controls the system. This function operates in cooperation with the smart key system.
HINT:
In this chapter, the expression "power source" has been used in some locations to allow precise explanations. The power source mode is also expressed using conventional expressions such as "engine switch off", "engine switch on (ACC)" and "engine switch on (IG)".
2. FUNCTION OF MAIN COMPONENTS
|
Component |
Function |
|---|---|
|
Engine Switch |
|
|
Electrical Key |
Receives signals from oscillators and returns ID code to entry door control receiver. |
|
Electrical Key Oscillator
|
Receives request signals from certification ECU (smart key ECU assembly) and forms detection area in vehicle. |
|
Power Management Control ECU |
|
|
Certification ECU (smart key ECU assembly) |
Certifies ID code received from entry door control receiver. |
|
Stop Light Switch |
Outputs state of brake pedal to power management control ECU. |
|
Steering Lock Actuator Assembly (steering lock ECU) |
Included in steering lock actuator assembly. Activates steering lock motor based on permission signals from power management control ECU. Receives lock/unlock request signals from certification ECU (smart key ECU assembly) and power management control ECU. Detects steering lock/unlock positions and transmits status to other ECUs. |
3. SYSTEM FUNCTION
The electric controls of the push-button start function are described below:
|
Control |
Outline |
|---|---|
|
Engine switch control |
When the person carrying the key enters the vehicle and the brake pedal is depressed, the power management control ECU sends the key certification request signal to the certification ECU (smart key ECU assembly). On receiving the key certification request signal, the certification ECU (smart key ECU assembly) generates a request signal and sends it to the indoor electrical key oscillator. The indoor electrical key oscillator transmits the request signal in order to detect that the key is in the cabin. When the key receives the request signal, it sends back the response code and ID code. When the door control receiver assembly receives the signal from the key, it sends the ID code to the certification ECU (smart key ECU assembly). The certification ECU (smart key ECU assembly) then matches the received ID code with the memorized code to determine if the key is one that has been registered. If the ID codes match, the certification ECU (smart key ECU assembly) sends the certification OK signal to the power management control ECU. Upon receiving the certification OK signal, the power management control ECU illuminates the engine switch indicator light, changes the power source mode and starts the engine depending on how the engine switch is operated. |
|
Diagnosis |
When the power management control ECU detects a malfunction, the power management control ECU diagnoses and memorizes information related to the fault. |
4. CONSTRUCTION AND OPERATION
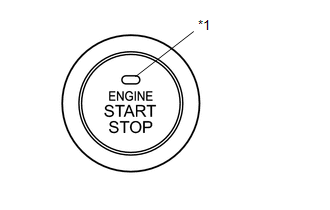
Text in Illustration
|
*1 |
Indicator Light |
(a) Engine Switch
The engine switch consists of a momentary type switch, 3 color (amber, green, clear blue) LEDs, and a transponder key amplifier.
- The clear blue LED is for illumination.
- The amber and green LEDs are for the indicator lights. The driver can check the present power source mode and whether the engine can start in accordance with the illumination state of the indicator light.
- When the power management control ECU detects an abnormality in the push-button start system, it makes the amber indicator light flash. If the engine stopped in this state, it may not be possible to restart it.
(b) Indicator Light Condition
Engine Switch Indicator Light Condition
|
Power Source Mode/Condition |
Indicator Light Condition |
|
|---|---|---|
|
Brake pedal released |
Brake pedal depressed, shift lever in P or N |
|
|
off |
off |
Turns on (Green) |
|
on (ACC, IG) |
Turns on (Amber) |
Turns on (Green) |
|
Engine running |
off |
off |
|
Steering lock not unlocked |
Flashes (Green) for 15 seconds |
Flashes (Green) for 15 seconds |
|
System malfunction |
Flashes (Amber) for 15 seconds |
Flashes (Amber) for 15 seconds |
(c) Power Management Control ECU
The power management control ECU consists of the IG1 and IG2 relay actuation circuits and CPU.
HINT:
Before removing the battery, make sure to turn the engine switch off. The power management control ECU constantly stores the present power source mode in its memory. Therefore, if the power supply for the power management control ECU is interrupted by disconnecting the battery, the power management control ECU restores the power source mode after the battery is reconnected. For this reason, if the battery is disconnected when the engine switch is in a condition other than off, the power will be restored to the vehicle at the same time the power is restored to the power management control ECU (by reconnecting the battery).
5. PUSH-BUTTON START FUNCTION OPERATION
(a) This system has different power source mode patterns depending on the brake pedal condition and shift lever position.
|
Brake Pedal |
Shift Lever |
Power Source Mode Pattern |
|---|---|---|
|
Depressed |
P or N |
When the engine switch is pushed once.
|
|
Not depressed |
P |
Each time the engine switch is pushed.
|
|
Except P |
Each time the engine switch is pushed.
|
|
|
- |
P |
When the engine switch is pushed in the on (IG) condition (engine running).
|
|
- |
Except P |
When the engine switch is pushed in the on (IG) condition (engine running).
|
When the key battery is low, the push-button start function can be operated by holding the key against the engine switch.
- After approximately 20 minutes has passed with the engine switch on (ACC) and the shift lever in P, the power management control ECU will automatically cut the power supply (the power source mode changes to off).
-
The illustration below shows the transition of power source modes.
Transition of power source modes:
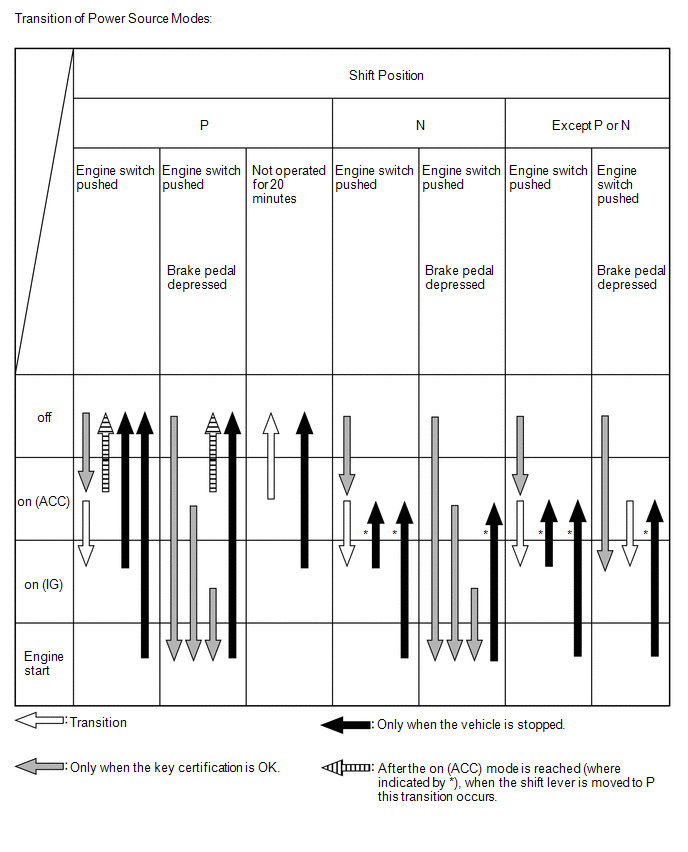
HINT:
While the vehicle is being driven normally, operation of the engine switch is disabled. However, if the engine must be stopped in an emergency while the vehicle is being driven, pressing the engine switch 3 times quickly or pressing and holding the engine switch for 2 or 3 seconds or more stops the engine. The power source mode will change from start to on (ACC).
6. WHEN KEY BATTERY IS LOW
(a) To operate the push-button start function when the key battery is low, hold the key close to the engine switch with the brake pedal depressed.
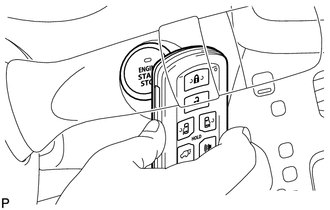
(b) The power management control ECU transmits a key verification request signal to the certification ECU (smart key ECU assembly) when it receives the stop light switch signal.
(c) The certification ECU (smart key ECU assembly) does not receive an ID code response from the entry door control receiver, so it actuates the transponder key amplifier built into the engine switch.
(d) The transponder key amplifier outputs an engine immobiliser radio wave to the key.
(e) The key receives the radio wave, and returns a radio wave response to the transponder key amplifier.
(f) The transponder key amplifier combines the key ID codes with the radio wave response, and transmits it to the certification ECU (smart key ECU assembly).
(g) The certification ECU (smart key ECU assembly) judges and verifies the ID code, and transmits a key verification OK signal to the power management control ECU. The buzzer in the combination meter sounds at the same time.
(h) After the buzzer sounds, if the engine switch is pressed within 5 seconds with the brake pedal not depressed, the power source mode changes to on (ACC) or on (IG), the same as in the normal condition.
7. DIAGNOSIS
The power management control ECU can detect malfunctions in the push-button start function when the power source mode is on (IG).
When the ECU detects a malfunction, the amber indicator light of the engine switch flashes to warn the driver. At the same time, the ECU stores a 5-digit Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) in its memory.
- The indicator light warning continues for 15 seconds even after the power source mode is changed to off.
- The DTC can be read by connecting the Techstream to the DLC3.
- The push-button start function cannot be operated if a malfunction occurs.
|
|
|